Building an AI-Powered RAG System with n8n and Qdrant
In this blog, we’ll explore how to build a complete RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system using n8n, Qdrant vector database, and OpenAI. This system allows you to upload documents, store them as embeddings, and then query them using an AI-powered chatbot that retrieves relevant information from your knowledge base.
What is RAG?
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It’s a technique that combines the power of large language models with a searchable knowledge base. Instead of relying solely on the AI model’s training data, RAG systems retrieve relevant information from your documents before generating responses, making answers more accurate and up-to-date.
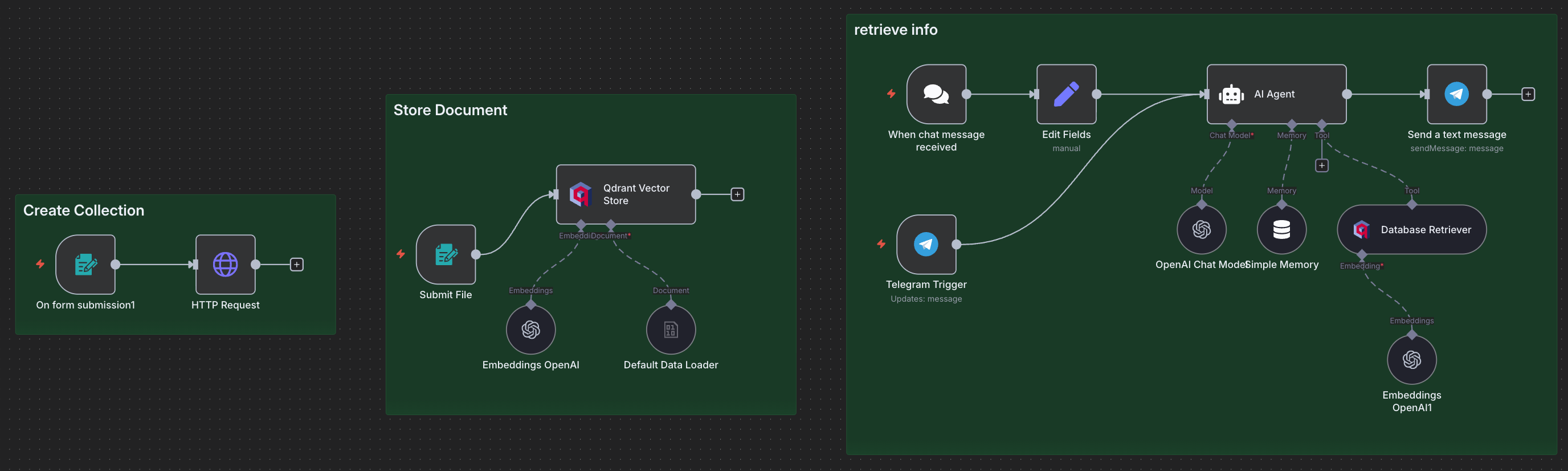
System Architecture
Our RAG system consists of three main components:
- Collection Creation - Set up a Qdrant vector database collection
- Document Storage - Upload and embed documents into the vector database
- Information Retrieval - Query the knowledge base through an AI agent
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- n8n instance (self-hosted or cloud)
- Qdrant instance (local or cloud)
- OpenAI API key
- Basic understanding of n8n workflows
Part 1: Creating a Qdrant Collection
The first step is to create a collection in Qdrant to store our document embeddings.
Workflow Components
Form Trigger Node:
This creates a web form where you can input the collection name.
Configuration:
- Form Title: “Create Qdrant Collection”
- Field Label: “Collection name”
- Required: Yes
HTTP Request Node:
This node creates the collection in Qdrant using the REST API.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"method": "PUT",
"url": "http://qdrant:6333/collections/",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"vectors": {
"size": 1536,
"distance": "Cosine"
}
}
}
The vector size of 1536 matches OpenAI’s embedding dimensions, and we use Cosine distance for similarity matching.
Part 2: Storing Documents in the Vector Database
Now let’s build the workflow to upload and process documents.
Workflow Components
1. Form Trigger (Submit File)
Create a form that accepts PDF files:
Configuration:
- Form Title: “add documents”
- Field Type: File upload
- Accept File Types: .pdf
- Required: Yes
2. Default Data Loader
This node extracts text content from the uploaded binary file (PDF).
Configure it with:
- Data Type: Binary
- This automatically processes the file and prepares it for embedding
3. Embeddings OpenAI
This node converts your documents into vector embeddings using OpenAI’s embedding model:
- Connect your OpenAI API credentials
- Uses the default embedding model (text-embedding-ada-002)
- No special configuration needed
4. Qdrant Vector Store
This is the heart of the storage workflow:
Configuration:
- Mode: Insert (to add new documents)
- Collection: “Qradar-Documentation” (or your collection name)
- Connect your Qdrant API credentials
Connection Flow
The workflow connects as follows:
- Form Trigger (Submit File) → Qdrant Vector Store
- Default Data Loader → Qdrant Vector Store (document input)
- Embeddings OpenAI → Qdrant Vector Store (embedding input)
The Default Data Loader connects to the document input of Qdrant Vector Store, while Embeddings OpenAI connects to the embedding input.
Part 3: Building the AI Agent for Retrieval
The final and most exciting part is creating an AI agent that can chat with users and retrieve information from your knowledge base.
Workflow Components
1. Chat Trigger (When chat message received)
This node creates a chat interface where users can interact with your AI agent. It automatically handles the conversation flow and provides a webhook URL for the chat interface.
2. AI Agent
The central node that orchestrates the entire conversation:
System Message:
1
You are a helpful assistant, refer knowledge to answer questions (use database retrieval tool)
The system message instructs the AI to use the retrieval tool when answering questions.
3. OpenAI Chat Model
Configure the language model:
- Model: gpt-4.1-mini (or your preferred model)
- Connect your OpenAI API credentials
- This provides the conversational AI capabilities
4. Simple Memory (Buffer Window)
This node maintains conversation context, allowing the AI to remember previous messages in the chat session. It uses a buffer window approach to keep recent messages.
No special configuration needed - just add it to the workflow.
5. Database Retriever (Qdrant Vector Store)
This is configured in retrieval mode to act as a tool for the AI agent:
Configuration:
- Mode: retrieve-as-tool
- Tool Description: “use this tool to fetch knowledge from the database”
- Collection: “Qradar-Documentation” (match your storage collection)
- Connect your Qdrant API credentials
6. Embeddings OpenAI (for retrieval)
Another embeddings node that converts user queries into vectors for similarity search in the database.
- Connect your OpenAI API credentials
- Uses the same model as the storage embeddings
Connection Flow
The retrieval workflow connects as follows:
- Chat Trigger → AI Agent
- OpenAI Chat Model → AI Agent (language model input)
- Simple Memory → AI Agent (memory input)
- Database Retriever → AI Agent (tool input)
- Embeddings OpenAI → Database Retriever (embedding input)
How It All Works Together
Document Upload Process
- User submits a PDF through the form
- Default Data Loader extracts text from the PDF
- Text is chunked into manageable pieces
- OpenAI generates embeddings (1536-dimensional vectors) for each chunk
- Embeddings are stored in Qdrant with the original text
Query Process
- User sends a question through the chat interface
- AI Agent receives the message
- User’s question is converted to an embedding
- Qdrant performs similarity search to find relevant document chunks
- Retrieved context is provided to the OpenAI Chat Model
- AI generates a response based on both the question and retrieved context
- Response is sent back to the user
Key Configuration Tips
Qdrant Settings
- Vector Size: Must match your embedding model (1536 for OpenAI)
- Distance Metric: Cosine is recommended for text embeddings
- Collection Name: Use descriptive names for different knowledge bases
Example: If you’re creating a documentation assistant for QRadar, name it “Qradar-Documentation”
OpenAI Settings
- Embedding Model: text-embedding-ada-002 (default and recommended)
- Chat Model: Choose based on your needs:
- gpt-4.1-mini: Best balance of speed and quality
- gpt-4: Higher quality but slower and more expensive
- gpt-3.5-turbo: Faster and cheaper but lower quality
- System Message: Clearly instruct the AI to use the retrieval tool
Memory Management
- Buffer Window Memory keeps recent conversation history
- Adjust window size based on your use case
- Larger windows provide more context but use more tokens
- Default settings work well for most use cases
Use Cases
This RAG system is perfect for:
- Technical Documentation - Create a chatbot for your product docs (like QRadar documentation)
- Knowledge Base - Internal company knowledge assistant
- Customer Support - Automated support with accurate information
- Research Assistant - Query through research papers and articles
- Personal Knowledge Management - Chat with your notes and documents
- Training Materials - Interactive learning assistant for training content
Real-World Example: QRadar Documentation Assistant
To illustrate how this RAG system works in practice, let’s look at a real implementation - a QRadar documentation assistant that helps security analysts quickly find information across multiple IBM QRadar guides.
Documents Added to the Knowledge Base
In this example, the following IBM QRadar PDF documents were uploaded to the vector database:
- b_qradar_users_guide.pdf - Comprehensive user guide for daily operations
- b_qradar_admin_guide.pdf - Administrator guide for system configuration
- b_qradar_admin_guide 2.pdf - Additional administrative documentation
- b_siem_installation.pdf - Installation procedures and requirements
- b_siem_deployment.pdf - Deployment architectures and best practices
- Threat Hunting Report.pdf - Threat hunting methodologies and use cases
- b_qradar_HA_guide.pdf - High availability configuration guide
- b_qradar_upgrade.pdf - Version upgrade procedures
How Users Interact with the System
Once these documents are uploaded and embedded, security analysts can ask questions like:
Installation Questions:
- “How do I install QRadar on VMware?”
- “What are the minimum hardware requirements for QRadar SIEM?”
- “How do I configure the second disk for /store partition?”
Operational Questions:
- “How do I create custom rules in QRadar?”
- “What’s the process for investigating a security offense?”
- “How do I configure log sources?”
Administrative Questions:
- “How do I set up high availability for QRadar?”
- “What’s the upgrade path from version 7.4 to 7.5?”
- “How do I backup and restore QRadar configuration?”
Threat Hunting Questions:
- “What are best practices for threat hunting in QRadar?”
- “How do I identify lateral movement in my network?”
- “What AQL queries are useful for detecting suspicious activity?”
Benefits of This Approach
Instead of manually searching through eight different PDF documents (potentially thousands of pages), the AI agent:
- Instantly retrieves relevant sections from all documents simultaneously
- Combines information from multiple guides when needed
- Provides direct answers with context from the documentation
- Remembers conversation history to handle follow-up questions
- Works 24/7 without getting tired or forgetting details
Example Query Flow
User: “How do I install QRadar on AWS?”
What happens behind the scenes:
- Query is embedded into a vector
- Qdrant searches across all 8 documents
- Finds relevant sections from
b_siem_installation.pdf - Also finds related AWS-specific information from
b_siem_deployment.pdf - AI Agent synthesizes both sources into a clear answer
AI Response: “To install QRadar on AWS, you need to use the Amazon Marketplace image. First, subscribe to IBM QRadar in the AWS Marketplace, then launch an EC2 instance with at least 8 vCPU and 16GB RAM (c6a.2xlarge or larger). You’ll need two disks: 125GB for root and 250GB for /store partition. After launching, SSH to the instance and run sudo /root/setup 3199 for an All-in-One console installation…”
This response combines information that might have been scattered across multiple pages and documents!
Adding Your Own Documentation
You can follow the same approach for any technical documentation:
- Gather your PDFs - Collect all relevant documentation files
- Upload through the form - Use the file submission form one by one
- Wait for processing - Each document takes a few seconds to minutes depending on size
- Test with questions - Ask questions to verify documents are properly indexed
- Iterate and improve - Add more documents or update existing ones as needed
The same system works for:
- Product documentation (Splunk, Elastic, etc.)
- Internal runbooks and procedures
- Training materials and guides
- Security policies and compliance documents
- Troubleshooting guides and FAQs
Best Practices
Document Chunking: Break large documents into smaller, focused chunks for better retrieval. Large documents should be split into sections.
Metadata: Add metadata to your documents for filtering and better context. This helps narrow down searches.
- Testing: Test with various question types to ensure accurate retrieval:
- Direct questions
- Conceptual queries
- Multi-step questions
Monitoring: Keep track of retrieval accuracy and adjust as needed. Check if the AI is actually using the retrieval tool.
Updates: Regularly update your knowledge base with new information. Remove outdated documents.
- Clear Instructions: Make your system message specific about when and how to use the retrieval tool.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Documents Not Being Retrieved
If the AI isn’t finding your documents:
- Check if embeddings are being generated correctly in the storage workflow
- Verify Qdrant connection and collection exists
- Ensure vector dimensions match (1536 for OpenAI)
- Test the Qdrant API directly to confirm documents are stored
Inaccurate Responses
If responses don’t match your documents:
- Review your system message to emphasize using the retrieval tool
- Check if relevant documents are actually in the database
- Consider adjusting retrieval parameters (top_k, threshold)
- Try asking more specific questions to test retrieval
Performance Issues
If the system is slow:
- Optimize document chunking size (smaller chunks = faster but less context)
- Use appropriate OpenAI model (mini models are faster)
- Consider caching frequently asked questions
- Check your Qdrant instance performance
Connection Errors
If workflows aren’t connecting:
- Verify all credentials are properly configured
- Check webhook URLs are accessible
- Ensure Qdrant service is running (especially for local instances)
- Test each node individually before connecting them
Extending the System
You can enhance this basic RAG system by:
- Multiple Collections: Create separate collections for different topics
- Example: One for technical docs, one for FAQs, one for policies
- Document Preprocessing: Add nodes to clean and format documents
- Remove headers/footers
- Extract specific sections
- Convert formats (Word, Excel, etc.)
- Metadata Filtering: Filter by document type, date, or category
- Add tags to documents
- Filter by date ranges
- Separate by department or project
- Hybrid Search: Combine vector search with keyword search
- Use both semantic and exact matching
- Better for technical terms and specific names
- Feedback Loop: Add user feedback to improve retrieval quality
- Thumbs up/down on responses
- Track which documents were most helpful
- Refine based on user behavior
Multi-Language Support: Add translation nodes for international teams
- Access Control: Implement user authentication and document-level permissions
Advanced Tips
Optimizing Embeddings
- Use larger chunks (500-1000 tokens) for conceptual information
- Use smaller chunks (100-300 tokens) for specific facts
- Overlap chunks by 20-50 tokens for better context
Improving Response Quality
- Adjust the system message based on your domain
- Add few-shot examples in the system message
- Use temperature settings to control response creativity
- Implement response validation before sending to users
Cost Optimization
- Cache embeddings to avoid regenerating for same documents
- Use gpt-3.5-turbo for simple queries, gpt-4 for complex ones
- Implement query classification to route appropriately
- Monitor token usage and set limits
Production Considerations
Before deploying to production:
- Security:
- Secure your webhook URLs
- Implement authentication
- Sanitize user inputs
- Protect API keys
- Scalability:
- Consider Qdrant cloud for better performance
- Monitor n8n execution times
- Implement rate limiting
- Add error handling and retries
- Monitoring:
- Track successful vs failed executions
- Monitor response times
- Log user queries for analysis
- Set up alerts for failures
- Backup:
- Regular backups of Qdrant collections
- Export n8n workflows periodically
- Document your configuration
Conclusion
Building a RAG system with n8n is straightforward and powerful. The visual workflow makes it easy to understand and modify the system. With Qdrant’s vector database and OpenAI’s models, you can create a production-ready AI assistant that provides accurate, contextual responses based on your own documents.
The beauty of this approach is its flexibility - you can adapt it to any domain by simply changing the documents you upload and adjusting the system message. Whether you’re building a documentation assistant for IBM QRadar, a customer support bot, or a personal knowledge assistant, the same architecture applies.
What’s Next?
In upcoming blogs, we’ll explore:
- Advanced RAG techniques (re-ranking, query expansion)
- Multi-modal RAG (images, tables, charts)
- Evaluating and optimizing RAG performance
- Deploying n8n workflows in production
- Building custom n8n nodes for specialized tasks
Thanks for reading, and happy building!
Quick Reference
Node Summary
Collection Creation:
- Form Trigger (collection name input)
- HTTP Request (Qdrant API call)
Document Storage:
- Form Trigger (file upload)
- Default Data Loader (extract text)
- Embeddings OpenAI (generate vectors)
- Qdrant Vector Store (store embeddings)
Information Retrieval:
- Chat Trigger (user interface)
- AI Agent (orchestration)
- OpenAI Chat Model (language generation)
- Simple Memory (conversation context)
- Database Retriever (vector search)
- Embeddings OpenAI (query embedding)
Required Credentials
- OpenAI API key (for embeddings and chat)
- Qdrant API credentials (for vector storage)
Key Parameters
- Vector Size: 1536 (OpenAI standard)
- Distance Metric: Cosine
- Collection Name: Your choice (descriptive name recommended)
- Embedding Model: text-embedding-ada-002
- Chat Model: gpt-4.1-mini (or your preference)
Useful Resources
- n8n Documentation: https://docs.n8n.io
- Qdrant Documentation: https://qdrant.tech/documentation
- OpenAI API Documentation: https://platform.openai.com/docs
- RAG Best Practices: https://www.pinecone.io/learn/retrieval-augmented-generation